Basic Electricity - Senior Secondary 2 - AC current generation
AC current generation
TERM: 1ST TERM
WEEK EIGHT
Class: Senior Secondary School 2
Age: 16 years
Duration: 40 minutes of 5 periods each
Date:
Subject: BASIC ELECTRICITY
Topic: AC CURRENT GENERATION
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, pupils should be able to
I.) Define and AC motor
II.) Identify the characteristics of an AC generator
III.) State the real life applications of AC generators
INSTRUCTIONAL TECHNIQUES: Identification, explanation, questions and answers, demonstration, videos from source
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS: Videos, loud speaker, textbook, pictures,
INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURES
PERIOD 1-2
|
PRESENTATION |
TEACHER’S ACTIVITY |
STUDENT’S ACTIVITY |
|
STEP 1 INTRODUCTION |
The teacher explains the meaning of AC motor and discusses the characteristics of an AC generator |
Students listens attentively to the teacher |
|
STEP 2 EXPLANATION |
Teacher state and describe some of the real life applications of AC generators. |
Students exhibit attentiveness and active engagement |
|
STEP 3 NOTE TAKING |
The teacher writes a summarized note on the board |
The students copy the note in their books |
NOTE
AC CURRENT GENERATION
An AC motor, or alternating current motor, is a type of electric motor that operates using alternating current (AC) as its power source. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive various mechanical devices.
Characteristics of an AC generator:
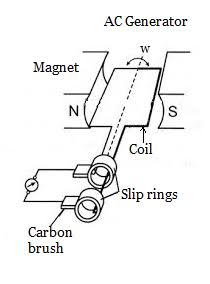
Real-life applications of AC generators
EVALUATION: 1. What is an AC motor?
CLASSWORK: As in evaluation
CONCLUSION: The teacher commends the students positively