Basic Electricity - Senior Secondary 1 - Structure of matter
Structure of matter
TERM: 1ST TERM
WEEK THREE
Class: Senior Secondary School 1
Age: 15 years
Duration: 40 minutes of 5 periods each
Date:
Subject: BASIC ELECTRICITY
Topic: STRUCTURE OF MATTER
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, pupils should be able to
I.) Define matter
II.) Describe the structure of matter
III.) Discuss the components of matter
IV.) Describe an atom
INSTRUCTIONAL TECHNIQUES: Identification, explanation, questions and answers, demonstration, videos from source
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS: Videos, loud speaker, textbook, pictures,
INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURES
PERIOD 1-2
|
PRESENTATION |
TEACHER’S ACTIVITY |
STUDENT’S ACTIVITY |
|
STEP 1 INTRODUCTION |
The teacher explains the meaning of matter and describe the structure of matter |
Students listens attentively to the teacher |
|
STEP 2 EXPLANATION |
Teacher identify and discuss the components of matter. Teacher discusses an atom and it's structure |
Students exhibit attentiveness and active engagement |
|
STEP 3 NOTE TAKING |
The teacher writes a summarized note on the board |
The students copy the note in their books |
NOTE
STRUCTURE OF MATTER
Matter refers to anything that occupies space and has mass. It's the substance that makes up everything around us, including solids, liquids, and gases. Examples of matter include solid objects like wood and metal, liquids such as water and oil, and gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide. Essentially, anything you can touch, see, or feel is made up of matter.
The structure of matter involves atoms as the fundamental units. Atoms comprise a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with electrons orbiting around the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
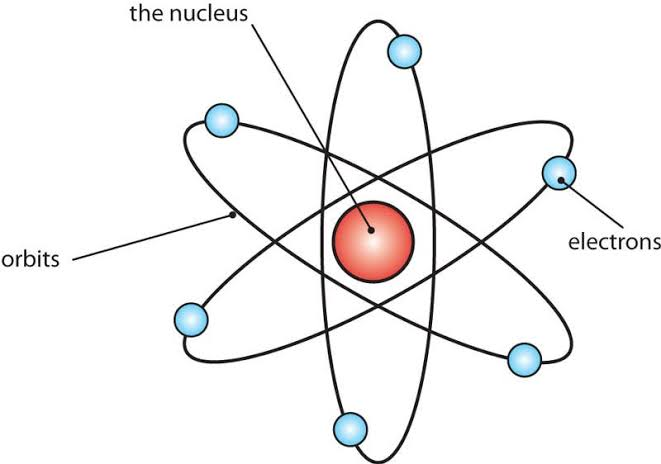
Components of matter
Structure of an atom

The structure of an atom involves a nucleus at its center, containing positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. Negatively charged electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels or shells, much like planets orbiting the sun. The nucleus provides most of the mass of an atom, while the electrons contribute to its size and chemical behavior.
EVALUATION: 1. What is matter?
CLASSWORK: As in evaluation
CONCLUSION: The teacher commends the students positively