Lesson Notes By Weeks and Term - Senior Secondary School 2
EXCRETORY SYSTEM IN MAMMALS AND PLANTS
SUBJECT: BIOLOGY
CLASS:� SS2
DATE:
TERM: 3RD TERM
REFERENCES
�
�
�
WEEK TWO
EXCRETORY SYSTEM IN MAMMALS AND PLANTS
CONTENT
�
EXCRETORY SYSTEM IN MAMMALS
Mammalian lungs excrete water vapour, and C02, the liver excretes bile pigment called bilirubin, the skin excretes water, salt and urea through the sweat, and the kidney excretes water, mineral salt and urea. The excretory system of mammals consists of a pair of kidney, ureter, bladder, renal artery and renal vein.
�
STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY
The mammalian kidney is a bean-shaped, reddish brown organ located in the posterior end of the abdomen. The right kidney is slightly lower in the body than the left. Cutting a kidney longitudinally, two distinct regions are observed; an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Several narrow tubules called urinary tubules (nephrons) pass through the two regions stated above. The tubules open at the tips of triangular- shaped masses of tissues called pyramids. The pyramids open into a funnel-shaped cavity called the pelvis. The kidney has many tiny capillaries which are branches of the renal artery and the renal vein. The pelvis continues as ureter, a long narrow tube connecting the kidney to the urinary bladder.
�
Diagram of the Kidney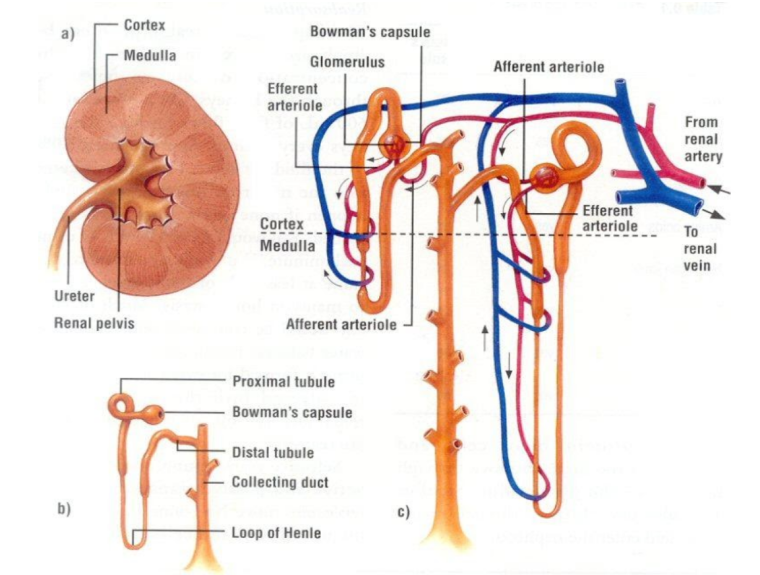
FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
The three major functions carried out by the kidney are as follows���
�
Osmoregulation: This is the process by which an animal regulates the balance between water and salt in their body fluid. When the concentration of the blood is higher than that of the cell content through the kidney extract or remove these substances from the blood so as to maintain normal osmotic balance in the body and vice-versa.�
�
Maintenance of Acid-Base Balance: The kidney excretes excess acids or bases when either of them is more concentrated in the body. If the body's concentration of base is higher than that of acid, more salt will be excreted with the urine as a result, acid-base balance is maintained in the body.Excretion: The kidney removes metabolic waste product from the body in form of urine. Urine formation is made possible by the numerous urinary tubules which are the functional units of the kidney.
�
EVALUATION
�
STRUCTURE OF THE URINARY TUBULE (NEPHRON)
The nephron consists of a cup-shaped Bowman's capsule which opens; into short coiled proximal convoluted tubules. The tubule continues as a U-shaped loop, the Henle's loop in the medulla, the loop re-enters the cortex as the distal convoluted tubule and widens as it enters the pelvis. The nephron is associated with several networks of capillaries. The renal artery branched in the Bowman's capsule formed a knot of capillaries called the glomerulus which re-joins to form a blood vessel leading out of the capsule and branches into a capillary network around the urinary tubule before joining the renal vein.
�
FORMATION OF URINE
ULTRA-FILTRATION: Blood is brought to the kidney by the renal artery, which enters the glomeruli (capillaries) in the Bowman's capsule. Water, mineral salt, sugar and other solute are filtered from blood into the capsule.
�
SELECTIVE RE-ABSORPTION: The glomerular filtrate flows down the tubules at the proximal convoluted tubular loop and the loop of Henle's where some watery sugar, amino acid and salt useful to the body are reabsorbed into the blood capillary by active transport. This process of reabsorption of useful materials back into the blood is called selective reabsorption.
�
HORMONAL SECRETION: As the fluid flows through distal convoluted tubules, more water is reabsorbed by the action of anti-diuretic hormones (ADH) and urine is finally formed. The urinary tubules empty their content into the pelvis and from the pelvis urine trickles through the ureter into the urinary bladder, which when full contracts and discharge urine out of the body through the urethra.
�
EVALUATION
�
EXCRETION IN PLANTS
Plants have no special excretory organs and excretory wastes are minimal. Elimination of waste takes place through the stomata and lenticels. Main waste products of plants arewater which is eliminated through transpiration and guttation and carbon dioxide from respiration at night when photosynthesis is not taking place. Other waste products in plants are alkaloids (quinine, nicotine, cocaine, morphine) products are converted into harmless substances, stored in some parts of the plants as useful commercial products.
�
GENERAL EVALUATION
�
READING ASSIGNMENT
College Biology Chapter 9, page 186-204
�
WEEKEND ASSIGNMENT
SECTION A
�
SECTION B
�
�
� Lesson Notes All Rights Reserved 2023