Lesson Notes By Weeks and Term - Junior Secondary School 3
RURAL AND URBAN WATER SUPPLY
TERM: 2ND TERM
SUBJECT: BASIC TECH
CLASS: JSS 3
Reference Materials
�
WEEK 7
TOPIC: RURAL AND URBAN WATER SUPPLY
�
CONTENT
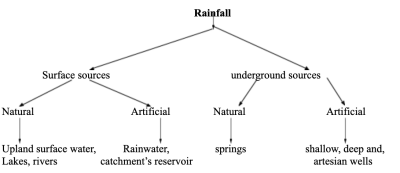
There are two main sources of water supply for rural and urban areas the surface sources and the underground sources
Sources of water are broadly classified as under ground sources and surface sources.�
Evaluation�
�
The surface sources are the lakes, rivers, upland surface water while the underground water includes the springs and wells.
�
SURFACE WATER: It originates from rainfall. It is a mixture of surface run off and ground water. This includes the rainwater collected directly from the roof, from the rivers, ponds and lakes and runs off from natural catchments into the natural or artificial lakes.
�
Rain water can be collected from the roofs of the building into the storage drums and tanks or buckets via overhanging collection trough. Rain water is the softest natural water, although it can be contaminated if the collecting surfaces are not well maintained
��
THE UNDERGROUND WATER: It is that portion of rainfall, which has percolated into the earth to form underground deposits. Examples include walls and springs.
Spring water is the water that has traveled as a result of its geological conditions. it is not different from wells.
�
Underground water is practical and safe in nature due to the following reasons:
�
Evaluation�
Ordinary raw water contains micro-organisms and dissolved substances which are a health hazard, and must therefore be removed by treating the water.
Water meant for human consumption must:
�
WATER PURIFICATION
The process by which water could be treated involves any of the following methods:
Clarification: This done to remove the suspended materials so that the water becomes clear.
Aeration: To remove various dissolved gases (methane, hydrogen sulphide, carbon dioxide etc)
Disinfect ion: This is the process of using chlorine to destroy undesirable organism in water, to improve coagulation of water, to control the odours in water and sludge in the purification chamber and to eliminate hydrogen sulphide in water.
Evaluation�
�
�
TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
Rural Water Supply is mainly from rivers and shallow wells. Water from the well can be brought to the surface manually or with the aid of a windless, hand pump or motorized pump.
There are two main pumps for pumping water- reciprocating plunger pump and the rotary pump. When the well is not the too deep (i.e.5m) the pump can be installed at the ground level. For deep wells, the pump is lowered down into the well.
Household treatment of water can be accomplished by boiling water and/or using water filter of appropriate grade (V or N or W)
�
Urban Water Supply: An urban water supply scheme (WSS) involves a collection or water impounding system (dam), a purification system, a transmission and distribution system.
The treatment of water involves the following processes: aeration, clarification, filtration and disinfection.
Pipelines are laid to convey treated water to the distribution reservoir, and the distribution lines to various service outlets.
�
The clear and pure water from the treatment plant is pumped through pipeline into the city reservoir for distribution to various service outlets���
Evaluation�
DISTRIBUTION RESERVOIR
Distribution reservoirs help to store excess water during the period of low demand and discharge it during the period of high demand. They are usually centrally located on an elevation to ensure distribution by gravity i.e. no pumping.����
�
This helps to maintain a regular water supply to meet the hourly variation of water demand. The reservoirs are sited on high position above the ground at least 10m higher than any storey building in that area. This is to ensure distribution by gravity.
�
Evaluation�
�
Reading Assignment
Read RURAL AND URBAN WATER SUPPLY
Reference Materials���
�
Weekend Assignment�
�
Theory���
� Lesson Notes All Rights Reserved 2023